Learn about Helth Discovery, which you hardly know about your body
स्वास्थ्य डिस्कवरी के बारे में जानें, जिसे आप अपने शरीर के बारे में शायद ही जानते हैं||
The human body is the entire structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
It comprises a head, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet.
The study of the human body involves anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions.
Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar and oxygen in the blood.
The body is studied by health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and by artists to assist them in their work.
Composition
Elements of the human body by mass. Trace elementsare less than 1% combined (and each less than 0.1%).
The human body is composed of elementsincluding hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calciumand phosphorus.[1] These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular components of the body.
The adult male body is about 60% water for a total water content of some 42 litres. This is made up of about 19 litres of extracellular fluid including about 3.2 litres of blood plasma and about 8.4 litres of interstitial fluid, and about 23 litres of fluid inside cells.[2] The content, acidity and composition of the water inside and outside cells is carefully maintained. The main electrolytes in body water outside cells are sodium and chloride, whereas within cells it is potassium and other phosphates.[3]
Cells
The body consists of many different types of tissue, defined as cells that act with a specialised function.[10] The study of tissues is called histology and often occurs with a microscope. The body consists of four main types of tissues – lining cells (epithelia), connective tissue, nervous tissue and muscle tissue.[11]
Cells that lie on surfaces exposed to the outside world or gastrointestinal tract (epithelia) or internal cavities (endothelium) come in numerous shapes and forms – from single layers of flat cells, to cells with small beating hair-like cilia in the lungs, to column-like cells that line the stomach. Endothelial cells are cells that line internal cavities including blood vessels and glands. Lining cells regulate what can and can't pass through them, protect internal structures, and function as sensory surfaces.[11]
Organs
Organs, structured collections of cells with a specific function,[12] sit within the body. Examples include the heart, lungs and liver. Many organs reside within cavities within the body. These cavities include the abdomen and pleura.
Circulatory system
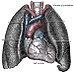
The circulatory system comprises the heartand blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries). The heart propels the circulation of the blood, which serves as a "transportation system" to transfer oxygen, fuel, nutrients, waste products, immune cells and signalling molecules (i.e., hormones) from one part of the body to another. The blood consists of fluid that carries cells in the circulation, including some that move from tissue to blood vessels and back, as well as the spleen and bone marrow.
Digestive system
The digestive system consists of the mouth including the tongue and teeth, esophagus, stomach, (gastrointestinal tract, small and large intestines, and rectum), as well as the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and salivary glands. It converts food into small, nutritional, non-toxic molecules for distribution and absorption into the body
Endocrine system
The endocrine system consists of the principal endocrine glands: the pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, parathyroids, and gonads, but nearly all organs and tissues produce specific endocrine hormones as well. The endocrine hormones serve as signals from one body system to another regarding an enormous array of conditions, and resulting in variety of changes of function.













No comments:
Post a Comment